Example to create a Mind Map – step by step
Renewable energy – Text source wikipedia
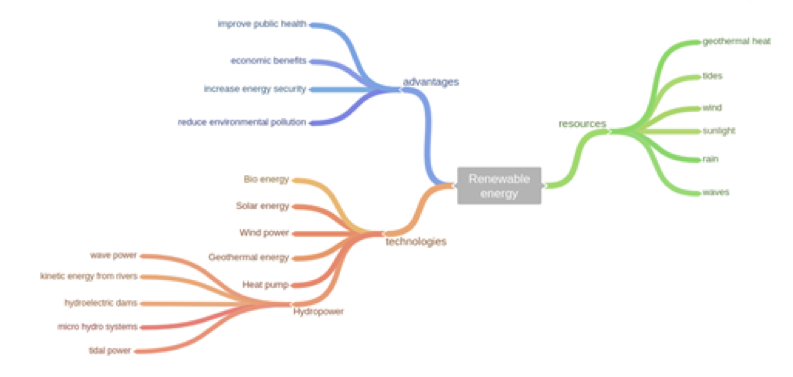
Renewable energy is generally defined as energy that comes from resources which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat.
Renewable energy replaces conventional fuels in four distinct areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/cooling, motor fuels, and rural (off-grid) energy services. Based on REN21‘s 2014 report, renewables contributed 19 percent to our global energy consumption. This energy consumption is divided as 9% coming from traditional biomass, 4.2% as heat energy (non-biomass), 3.8% hydro-electricity and 2% is electricity from wind, solar, geothermal, and biomass. Renewable energy resources and significant opportunities for energy efficiency exist over wide geographical areas, in contrast to other energy sources, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Rapid deployment of renewable energy and energy efficiency, and technological diversification of energy sources, would result in significant energy security and economic benefits. It would also reduce environmental pollution such as air pollution caused by burning of fossil fuels and improve public health, reduce premature mortalities due to pollution and save associated health costs. While many renewable energy projects are large-scale, renewable technologies are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development.
Mainstream technologies
- Wind power – Airflows can be used to run wind turbines.
- Hydropower – Energy in water. There are many forms of water energy:
- Hydroelectric energy is a term usually reserved for large-scale hydroelectric dams.
- Micro hydro systems are small hydroelectric power installations.
- Run-of-the-river hydroelectricity systems derive kinetic energy from rivers without the creation of a large reservoir.
- Wave power, captures the energy of ocean surface waves,
- Tidal power, converts the energy of tides,
- Solar energy – radiant light and heat from the sun, uses a range of technologies such as solar heating, photovoltaic, concentrated solar power, solar architecture and artificial photosynthesis. Solar technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on the way they capture, convert and distribute solar energy.
- Geothermal energy – is from thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth, like hot springs.
- Bio energy – biomass is biological material derived from living, or recently living organisms (wood remains, municipal solid waste, plant or animal matter). As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly via combustion to produce heat, or indirectly after converting it to various forms of biofuel. Conversion of biomass to biofuel can be achieved by different methods which are broadly classified into: thermal, chemical, and biochemical methods.
- Heat pump – are designed to move thermal energy opposite to the direction of spontaneous heat flow by absorbing heat from a cold space and releasing it to a warmer one. A heat pump uses some amount of external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink.
Mind map – in order to create the map you should follow the instructions from the course.
| Question | Answer |
| What is the main knowledge? | Renewable energy |
| What are the sub-nodes? | Ask some of the next questions: |
| What is the definition? | energy from natural resources: sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat |
| What are the advantages? | Advantages of using renewable energy: improve public health, economic benefits, increase energy security, reduce environmental pollution. |
| What are the technologies? | Technologies used to obtain renewable energy are: bio energy, solar energy, wind power, geothermal energy, heat pump, and hydropower. |
| What means hydropower? | Hydropower means: wave power, kinetic energy from rivers, hydroelectric dams, micro hydro systems, tidal power. |
In order to practice create one Mind Map for each of the following issues:
- The organisational structure of the school (eg, director, deputy director, board of directors, board of parents, the organisational structure of each class).
- Organise your weekly activities.
- Create the organizational structure of the European Union.
- Classification of olympic sports.
- Carrier classification.
- Common diseases.








